Abstract
Introduction: FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) mutation (m) is one of the most prevalent mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and it is associated with an increased risk of relapse and decreased overall survival (OS). The standard of care therapy for physically fit treatment naïve patients is intensive chemotherapy with FLT3 inhibitor (i) (midostaurin). For older/unfit patients, venetoclax-based induction is preferred as per NCCN guidelines. We explored the clinical outcome of FLT3m AML patients who were ineligible for intensive chemotherapy and treated with a hypomethylating agent (HMA) plus venetoclax (Ven) based induction at Mayo Clinic.
Methods: Thirty FLT3m AML patients who were ineligible for intensive chemotherapy and received HMA+Ven induction at Mayo Clinic between June 2019 and May 2022 were analyzed for clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes. Patients who received HMA+Ven for the relapsed or refractory disease were excluded. All patients received at least one cycle of HMA, either azacitidine (75 mg/m2 from day 1 to 7) or decitabine (20 mg/m2 from day 1 to 5). Responses were assessed according to the 2022 European Leukemia Net (ELN) criteria.
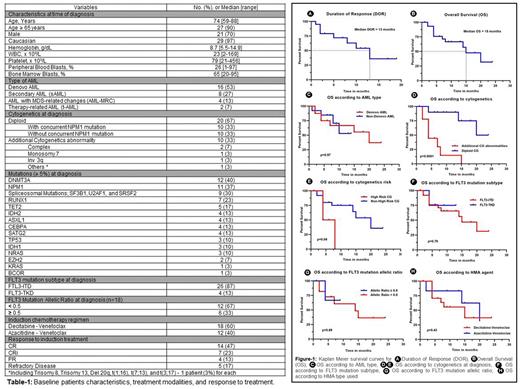
Results: The baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Most of the patients (n=27, 90%) were ≥ 65 years old with a median age of 74 years (range, 59 to 88). Majority of the patients (n=16, 53%) had de novo AML, 8 (27%) patients had secondary AML, 4 patients (13%) had primary AML with MDS-related changes, and 2 patients (7%) were diagnosed with therapy-related AML. Two-thirds of the patients (n=20, 67%) had diploid cytogenetics (CG) and 10 (33%) patients had additional cytogenetic (CG) abnormality at diagnosis. Twenty-six (87%) and 4 (13%) patients had FLT3 ITD and TKD mutation subtypes, respectively. The median baseline FLT3m allelic ratio was 0.39 (range, 0.1-0.7). Most frequent reported mutations (≥ 5%) were DNMT3A (40%), NPM1 (37%), spliceosome mutations (SF3B1, U2AF1, and SRSF2; 30%), RUNX1 (23%), and TET2 (17%). Seventy percent of the patients achieved complete remission with or without count recovery (CR/CRi) (n=21), 13% (n=4) of the patients had partial remission, and 17% (n=5) of the patients had refractory disease to HMA+Ven induction. The median time to achieve CR/CRi was 35 days (range, 22-230). Most CR/CRi patients (86%, n=18) continued consolidation therapy with HMA+Ven. Until changing the HMA+Ven regimen for any reason, the median number of HMA+Ven cycles received was 6 (range, 1-13). Only one patient received allogeneic stem cell transplant allo-HSCT after achieving remission and received gilteritinib maintenance therapy post-transplant. Six (29%) of the CR/CRi patients had relapse with a median time to relapse of 6 months (range, 1-10). The median duration of response was 13 months (95% CI: 6.71-19.28) (Figure 1A), and the median OS was 15 months (95% CI: 8.89-21.10) (Figure-1B). FLT3i (gilteritinib) was received in 6 patients (20%) post HMA+Ven; 2/6 received as maintenance therapy and 4/6 for relapse disease. In the univariate analysis for OS, diploid cytogenetics (p<0.0001) and non-high risk cytogenetics (p=0.04) were associated with significantly better OS (Figure-1D/E). AML sub-type (de novo vs sAML) (p=0.97), NPM1 mutation at diagnosis (p=0.39), FLT3m subtype (ITD vs TKD) (p=0.79) or allelic ratio at diagnosis (<0.5 vs >0.5) (p=0.89), and HMA sub-type (azacitidine vs decitabine) (p=0.43) were not significantly associated with difference in OS (Figure-1C/F/G/H, respectively).
Conclusions: In summary, HMA+ Ven showed significant activity in treatment naïve FLT3m AML patients who were ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. HMA+Ven can be used as a backbone in combination with FLT3 inhibitor to improve outcome further and for successful transition to curative intent therapy such as allo-HSCT.
Disclosures
Al-Kali:Astex: Other: research support to institution. Shah:Astellas: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Marker Therapeutics: Research Funding. Patnaik:Kura Oncology, Stem Line Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Foran:Novartis, Servier, Pfizer, BMS, Taiho: Other: Formal Advisory Activities; AbbVie, Actinium, Aptose, Astex, H3Biosciences, Kura Oncology, Trillium, Xencor: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal